*Complimentary Endoscope Information and Inspection Procedures! F.A.Q.
1800Endoscope.com
is not associated, endorses any information or links on this webpage and
information and links are not necessarily the views or opinions of
1800Endoscope.com
. Use at your own risk.

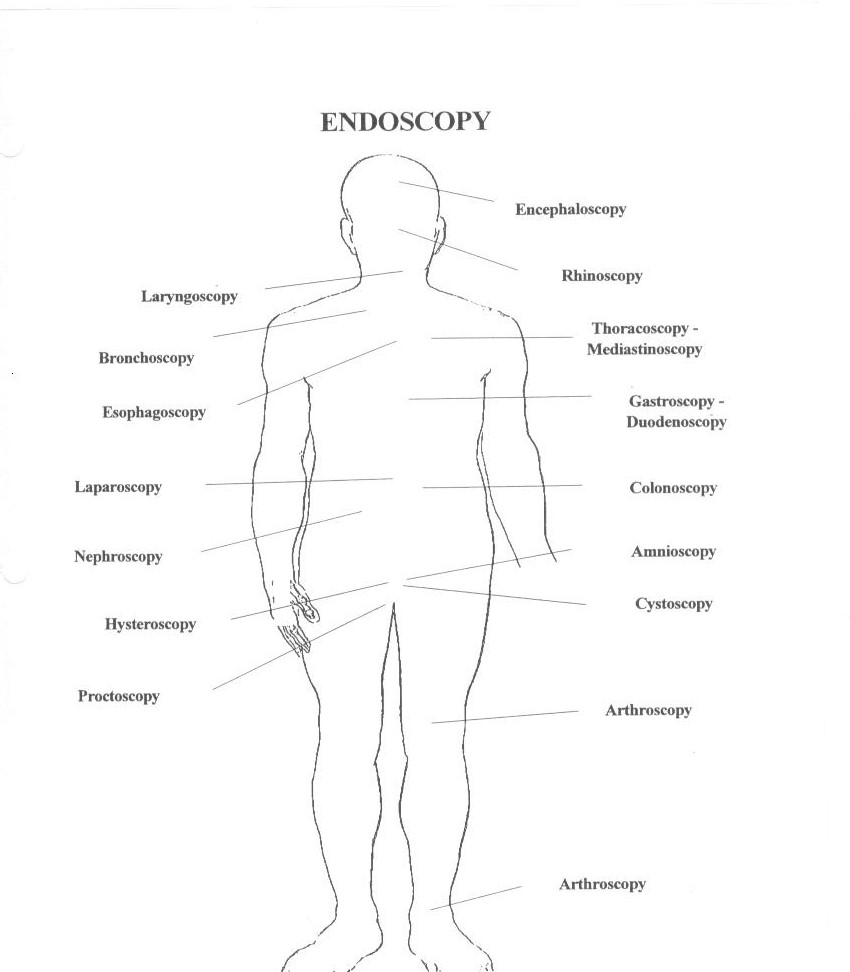
ENDOSCOPY TERMINOLOGY
"Endoscopy" is a general term. There are specific words for viewing specific parts and organs of the body. Endoscopy done through existing body openings can usually be done under local anaesthesia, but other types that require a small puncture to see an "internal cavity" may need hospital admission and a general anaesthetic. In each type small pieces of tissue can be removed for tests and some other procedures can be done. The following is a list of the major types of endoscopy.
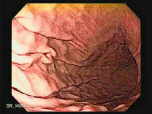
GASTROSCOPY: To see the gullet, stomach and upper small intestine.
ESOPHAGOSCOPY: Transnasal to see the gullet, stomach and upper small intestine
COLONOSCOPY: To see the large intestine.
CYSTOSCOPY: To see the urinary bladder.
BRONCHOSCOPY: To see the air passages to the lungs.
LARYNGOSCOPY: To see the larynx or voice box.
NASOPHARYNGOSCOPY: To see the nose and related cavities.
LAPAROSCOPY: To see the "stomach cavity" and the organs therein.
ARTHROSCOPY: To see inside joints such as the knee joint.
THORACOSCOPY: To see inside the chest cavity.
The medical name for upper endoscopy is esophagogastroduodenoscopy or EGD for short.
There are a number of other sub-types of "scopies", and these include proctoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, nephro-ureteroscopy, mediastinoscopy, choledochoscopy, angioscopy and others.
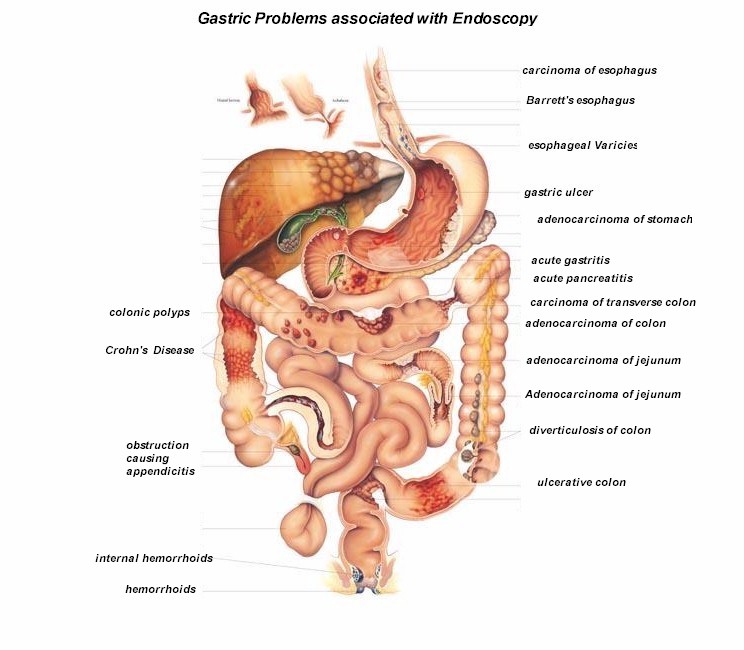
Get a full color chart like one above at Anatomical Chart Company Click here!
Its Amazing How many People Twitter: Endoscopy !
HISTORY OF ENDOSCOPES DR. MURRA
View Endoscopy Images:
( Warning: Graphic endoscopy photos )
http://www.gastrointestinalatlas.com
compliments of Dr. Murra Saca El Salvador
Watch live video from endoscopy on www.justin.tv
Watch an Short Endoscopy Procedure:
( brief .mpeg Click image )
requires: RealPlayer®
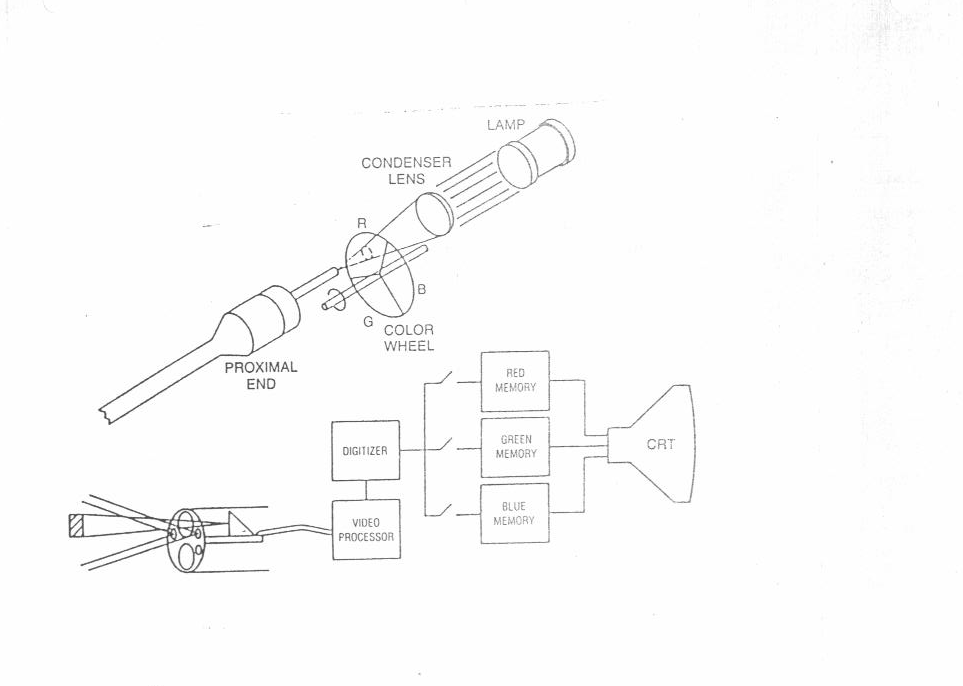
BASIC VIDEO ENDOSCOPE R.G.B. SYSTEM
Click here for
*Inspection Procedures for Most Flexible Endoscopes:
Purchase a full comprehensive training video on Inspecting
any endoscope!:
SPVTIP-VHS...Olympus®,Pentax®and
Fujinon® Inspection Procedures TRAINING
TAPE......$50.00
| *Flexible Endoscope INSPECTION PROCEDURES |
|
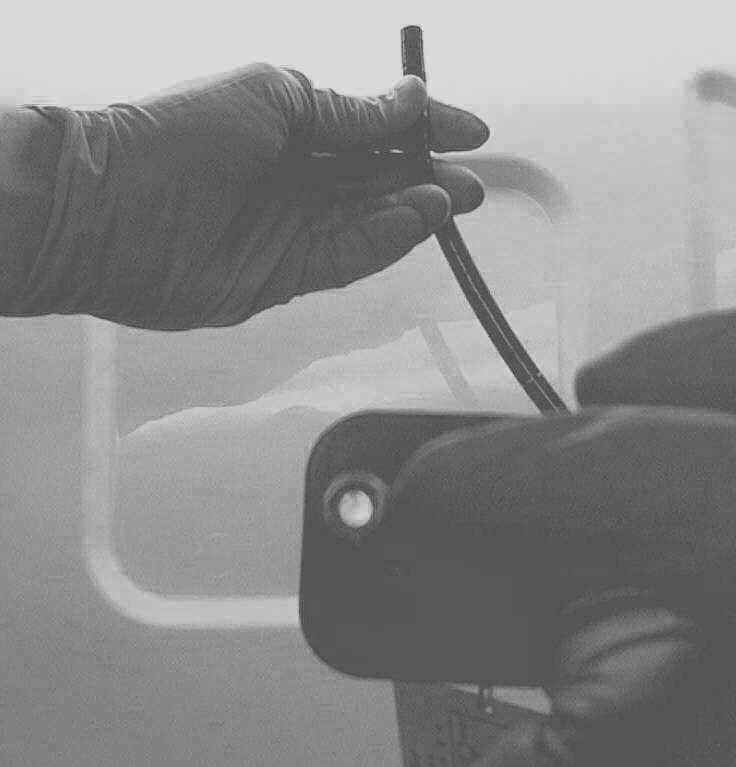
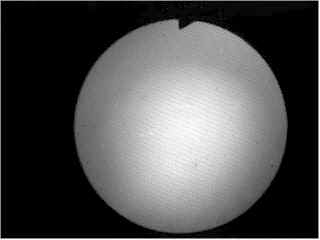
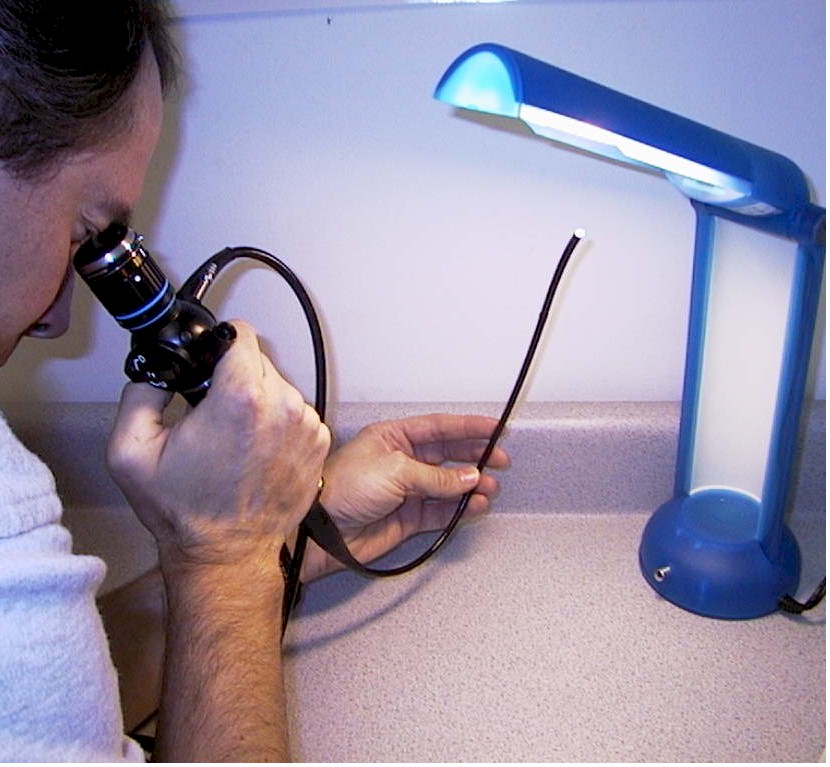
HOW TO CHECK FIBERSCOPES FOR BROKEN FIBERS! HOLD TIP OF SCOPE UP TO A LIGHT, LOOK THROUGH EYEPIECE AND FOCUS.
THIS SCOPE IS PERFECT, NO BLACK DOTS! 1) View the image: If fiberscope check for:
Broken fibers, Observe if any signs of fluid invasion; Stains, "Redcrack", X-Ray yellowing, image brightness etc. Also view eyepiece for dust, fluid contamination etc.
If checking a Videoscope; Put endoscope in processor, observe image for signs of fluid invasion ( foggy ) and picture break-up, ( angulate the scope by turning knobs). If Image is stained, redcrack repair will be required. If video picture has interference, a Major Fluid invasion or CCD repair is needed! How Fluid Invasion
Remember - fluid problems are a scopes worst enemy! How Image And Light Guide Problems Occur;
|
|
2) Plug Video scope into processor, test #1 , 2,3,4 Freeze frame buttons. If there is fluid invasion, buttons will either not work or cause constant freezing and beeping of Processor and will require replacement...
|
|
3) Observe Light guide illumination bundle by observing image, then unplug scope from light source, hold distal tip to a light and be sure it is not over %10 broken.
If over 10%, Illumination bundle will require replacement...
|
|
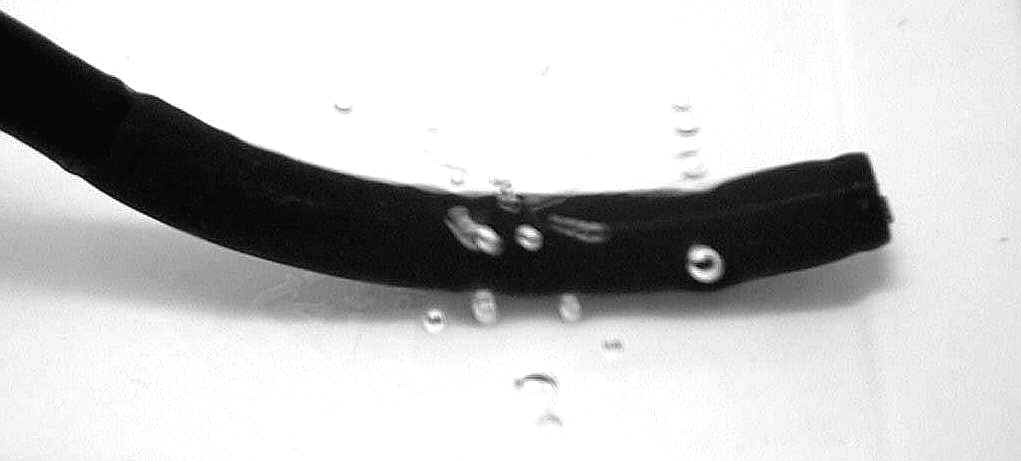
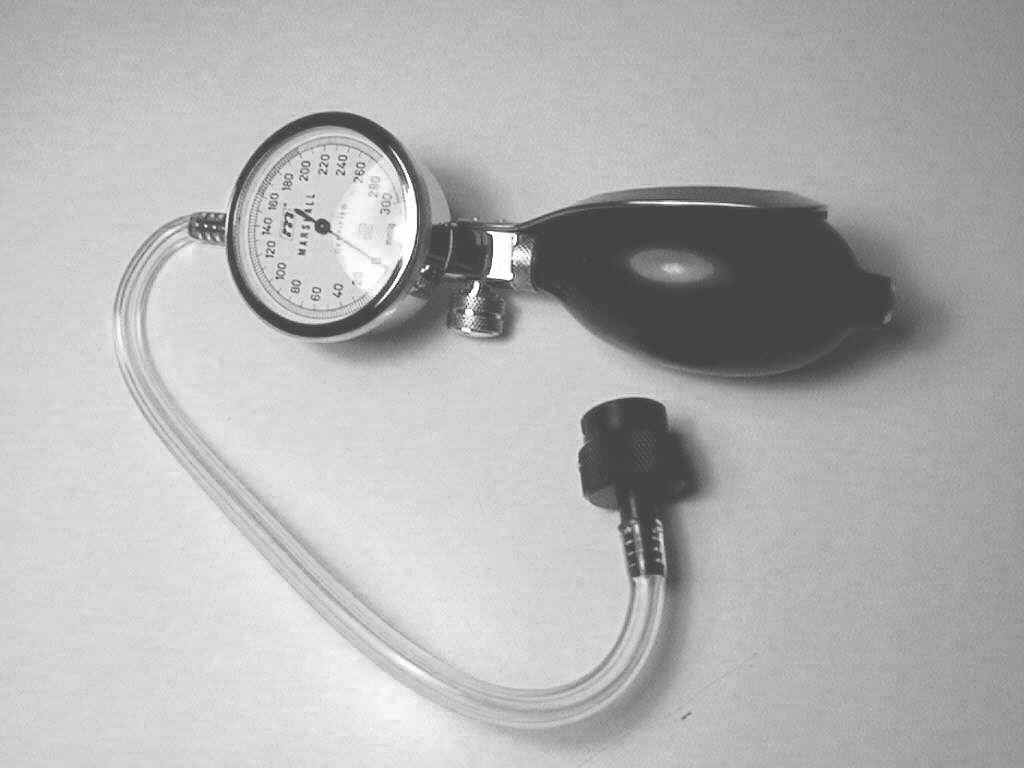
4) Test Air Leakage: use a air leakage tester and pump p endoscope with air: waiting 3 minutes @ 3.5 PSI Submerse endoscope in water and angulate endoscope to check for small leaks in bending rubber, insertion tube, light guide tube, body etc If leaks are found anywhere on endoscope, this may cause Fluid invasion, and endoscope will require Aeration immediately! How Bending Sheaths Become Damaged;
|
|
5) Test Air Water functions: With Endoscope plugged into light source or processor, and depressing air/water valve; water should spray out of nozzle over objective lens at least 30 cc's in 30 seconds, holding finger on air valve; 50cc's in 5 seconds using a measuring beaker...Water should shoot over objective lens. Be sure nozzle is not missing. If air or water is faulty or missing, air/water nozzle or channels will require unblocking or replacing... How Air/Water Problems Occur;
|
|
6) Test suction by connecting endoscope to suction pump and with suction on, depress suction valve with tip in 80cc of water, endoscope should allow 80 cc's in 5 seconds. If a groove is worn in suction port, suction will be decreased and will require replacement...
|
|
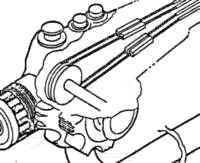
7) Using the correct size Biopsy Forceps, pass the Forceps through the endoscope biopsy channel and text for kinks in the channel. Angulate endoscope while passing through distal end of scope. If forceps do not pass or resistance is felt, channel(s) may require replacement... Biopsy Channel Damage Is Usually A Result Of:
|
|
8) Using the correct size cleaning brush, remove suction valve and pass through suction port till it is visible at suction port on connector, if any resistance is felt, suction channel will require replacement!
|
 ( represents bad buckles @ boot ) 9) Check Insertion tube; look for any holes ( as in step 4 will show leaks). Check for wear, wrinkled, blistered, buckles etc. Be sure that IT is not impacted, loose and twists@boot! If buckled @ boot, or anywhere on tube, insertion tube will require replacement!...
|
|
10) Check angulation; refering to manufacturers specifications,using angulation chart; angulate endoscope. Example: CF-100L: Up: 180°, Down 180°, Right 160°, Left 160°. Endoscope should angulate smoothly with no play. If angulation is tight or doesn't angulate at all,play and angles will require adjustment or angulation wire replaced. If bending section bends irregularly or to one side, bending section mesh or articulating section will require replacement... Angulation Problems
|
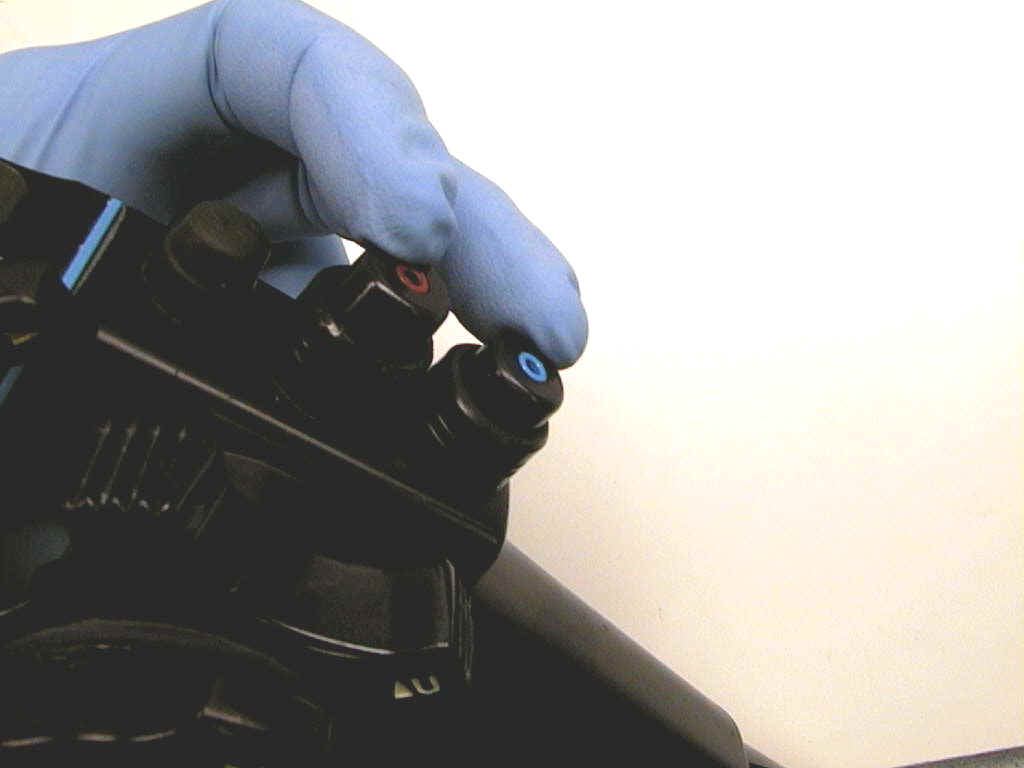
| 11) Check Knobs, turn
knobs back and forth. If they leak are loose or cracked. They will
require replacement. If a grinding feeling is
noticed on Pentax® or Fujinon®, drum wire will require replacement.
|
|
12) Check the Light guide tube (umbilical), and connector. Be sure there are no leaks,( as in step 4 will show leaks), buckles or wrinkled etc. Be sure connector has no loose parts, fluid in video connector etc. If it has a leak, buckled or impacted, replacement is required!
|
13) Observe the distal
end,  the
"c-cover" distal and cap should be round and smooth. Check
lenses, they shouldn't be cracked or dirty. Also the same for objective
lens. Check Biopsy channel hole, should be round and smooth. If
C-cover is impacted; cracked, will require replacement. If lenses are
cracked, they will distort light and will require replacement. If biopsy
channel is cut with laser, c-cover or channel will require repair. the
"c-cover" distal and cap should be round and smooth. Check
lenses, they shouldn't be cracked or dirty. Also the same for objective
lens. Check Biopsy channel hole, should be round and smooth. If
C-cover is impacted; cracked, will require replacement. If lenses are
cracked, they will distort light and will require replacement. If biopsy
channel is cut with laser, c-cover or channel will require repair.
|
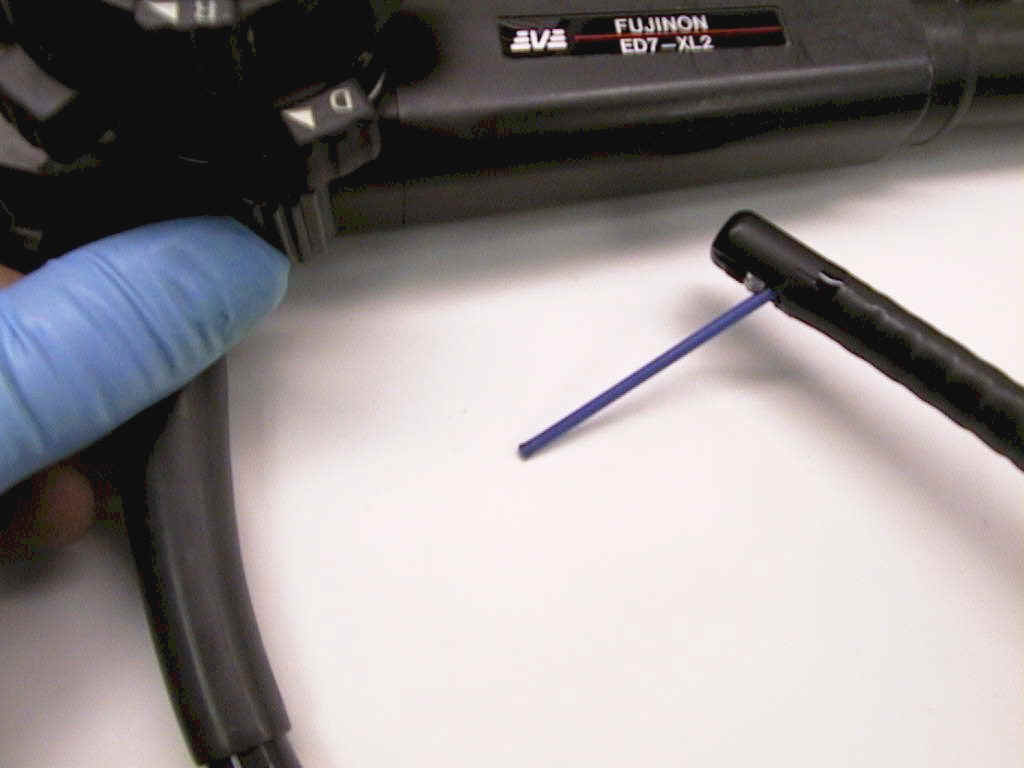

14) Duodenoscopes: Elevator wire check. With forcep down channel and pointing out of distal end approximately 1 inch, move Control arm lever, forcep should move up and down at distal end and observing image, should come into field of view at manufacturers specifications. If lever doesn't move elevator wire or is tight or stuck, elevator wire or lever assembly must be repaired or replaced. |

WIRING
DIAGRAMS FOR VIDEO SYSTEMS INFO!
F.A.Q.
|
Q: How often should endoscopes be checked for maintenance? Are there generally blatant signs when a scope is not working properly and should be checked? A: Scopes should be leak tested after every procedure and before disinfection. The most effective leak test is to submerse the entire scope and follow orignial equipment manufacturer (OEM) instructions. If a leak is detected, the scope needs to be sent in for repair immediately. Scopes should be checked for maintenance on a weekly, monthly, or quarterly basis depending on the number of scopes used and procedures performed. There are blatant signs that a scope should be checked. One of the most common is when a video scope starts taking pictures by itself, or when it will not take pictures. Usually this is a sign of fluid invasion. The fluid has entered the video switch block controls and the scope needs to be sent in for repair immediately. If a picture is cloudy on a video scope, users should look for a buildup of gluteraldehyde on the distal lens. If there is a buildup or debris on the lens, clean the lens with a rubbing alcohol wipe. If there is no buildup or debris on the lens, the video scope probably has fluid in the distal end. The scope needs to be sent in for repair immediately. If a fiber optic scope is cloudy, look for a buildup of gluteraldehyde or debris on the distal lenses. If there is no buildup or debris, look for fluid in the eyepiece and distal lenses. If there is any sign of fluid, send the scope in for repair immediately. Other signs are clicking and/or sluggishness in the angulation controls, significant movement of the insertion tube when angulating the distal end, poor light transmission, color fluctuations in the video image, blockage or friction when passing a brush through the biopsy and/or suction channel, poor water and/or air flow, poor suction and tears or significant dents in the insertion or light guide tube. Users should call their repair company and/or sales representative for inspection and/or advice. Another sign is fluid in the water resistant cap when it is removed after the disinfection process. If fluid is present, redo the leak test. If the leak test is negative, more than likely the water-resistant cap is not so water resistant. Leak test the water resistant cap. Scopes should be checked for rough edges, sharp nozzles, and cracking/deteriorating glue as all of the above can pose a significant risk to patient safety. Q: What are the most common repairs made to endoscopes? A:
Q: What services should endosuite managers be looking for in a company that offers to repair scopes? A: Honesty, , and customer service! Scope repair companies should be able to tell you why a repair is necessary. Test your repair company. Tell them you suspect a scope has a major fluid invasion, send it in for repair and see what they quote. If you are going to experience the cost savings of using an independent service organization, they must be honest. is equal to honesty. Check out the of their replacement parts. Without , pricing and turnaround time mean nothing. Last but of great importance as well is customer service. Everybody makes a mistake once in a while. How does the lab honor a warranty? Do they continually look for reasons to charge more money for their mistakes? The following are a couple good questions to ask:
What parts are used in the repair process? Specifically, what type of bending rubber glue is used? Some companies use glues.
Q: Are some scopes more fragile than others? Are there any brands known within the industry that generally require more repair than others? A: Small diameter fiber optic scopes are more fragile than other scopes. Special protection should be used during storage and transport. Each brand of scopes has advantages and disadvantages. For liability reasons, We cannot mention a particular OEM, but managers should look into the warranty and what kind of support they will receive after the purchase. If they are buying used equipment, make sure the company has their own repair capabilities. Some scopes are made to last and others are what we call resposable scopes. They are not made to be worked on. Once they break they typically require a major overhaul by the OEM. This defeats the purpose of buying a less expensive scope. Q: If a scope is treated ideally, how long is the expected lifespan? How long should endonurses and technicians expect to be able to trust a scope that has been repaired before worrying about sending it in again? A: Ideally a scope can last quite a long time but the life span depends upon the number of procedures and the number of scopes used to perform those procedures. Obviously an account with a sufficient number of scopes to meet the procedure volume will experience a greater life span. The lifespan also depends upon proper handling, use, care, and maintenance. A scope is typically not sent in for repair until it develops a problem. Obviously a scope repaired with parts and workmanship will last much longer than a scope repaired with low parts and poor workmanship. Q: How should scopes be treated to prevent excessive repair bills? A: Scopes should be treated according to OEM specifications. Most nurses and technicians do an excellent job in the handling of endoscopes. We recommend having dedicated cleaning personnel. This avoids the number of people involved in the handling process. Fewer people involved can reduce excessive repair expenses. Dedicated cleaning personnel can reduce repair bills by routinely performing proper cleaning and disinfection procedures as proscribed by the OEM. Familiarity with the scopes can prevent damage before it occurs. A technician familiar with the scopes can usually notice buckles or kinks in the channels and other signs as listed above that if detected would be a minor repair charge. Leak testing is by far the most important step in reducing repair expenses.
|
|
INSPECTION PROCEDURES BIOPSY FORCEPS |
| Handle should open jaws cleanly and smoothly. If jaws are locked shut, repair of jaws is required. If Handle broken, replacement required. |
| Observe coil pipe, they should be smooth and straight. If bent or twisted, coil pipe replacement is required. |

|
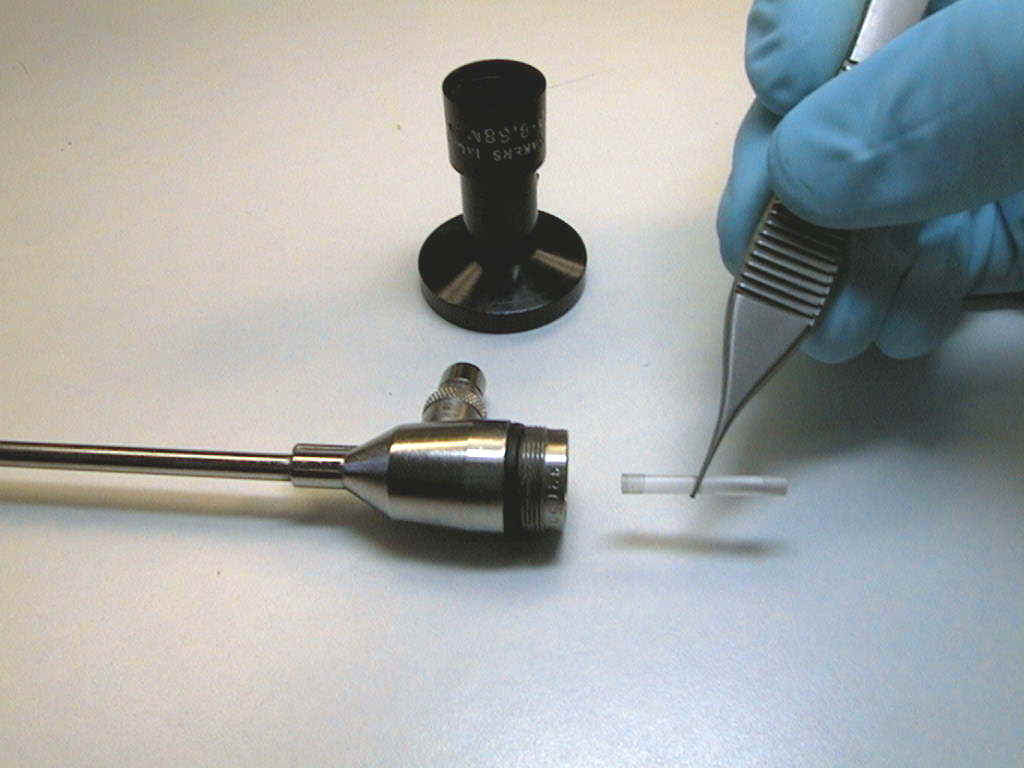
INSPECTION PROCEDURES RIGID ENDOSCOPE |
|
Observe eyepiece section. If dropped and damaged, eyepiece will require repair. |
|
Observe image, should be crystal clear. If foggy or any specs of dust or dirt, repair required: ( Eyepiece, rod lens, objective ). |
|
Observe
image, it should be crystal clear. If distorted or no image, repair
required: ( Eyepiece, rod lens, objective ). ( chipped Rod lens ) |
|
Externally view distal tip of endoscope, check objective system. If impacted and damaged at tip, repair required. ( Objective system ). |
|
Inspect the metal shaft of rigid endoscope, it should be straight. If impacted, bent and damaged at tip, repair required. ( Straighten or replace shaft, rod lenses, possible refiber ). |
|
Point the tip at a light, observe light post of rigid endoscope, it should be round and bright with less than 5% broken fibers. If more than 5% it will require re-fibering. |
Gastro Links +
!
1800Endoscope.com LLC
7322 Manatee Ave. West #265
Bradenton, FL. 34209 USA
800-363-6726
+ 941 209 8276 SMS / Text!
©Copyright Olympus®
* Inspection procedures are industry wide inspection tests. They may not be Manufacturers recommended inspection procedures.